Social Determinants of Health
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention defines the social determinants of health (SDoH) as the complex, integrated, and overlapping social structures and economic systems that include the social environment, physical environment, and health services, or the structural and societal factors that are responsible for most health inequalities. The SDoH are shaped by the distribution of money, power, and resources at global, national, and local levels, which are themselves influenced by policy choices. Structural racism has a significant impact on the Black community’s health outcomes and SDoH. While the data available to us are not disaggregated by race, we understand that conditions and outcomes are worse for Black populations.
Additional Resources
- Kaiser Family Foundation: Key Facts on Health and Health Care by Race and Ethnicity
- CDC: Health Equity Considerations and Racial and Ethnic Minority Groups
- Public Health Review: Improving the Health of African Americans in the USA: an Overdue Opportunity for Social Justice
The tools below explore various social determinants of health that affect the health of individuals in the community. Indicators are disaggregated by geography in order to compare St. Louis rates to Missouri rates to United States rates. Many of these data sources do not disaggregate data by race. Therefore, statistics are reflective of all populations. FLOURISH hopes data becomes more readily disaggregated by race for future updates. If disaggregation by race is available, colors will be used. If there is an X shown instead of a rate, that means the data are not available at that level. These are opportunities to explore new data collection methods and sources.
Social Determinants of Health
Housing
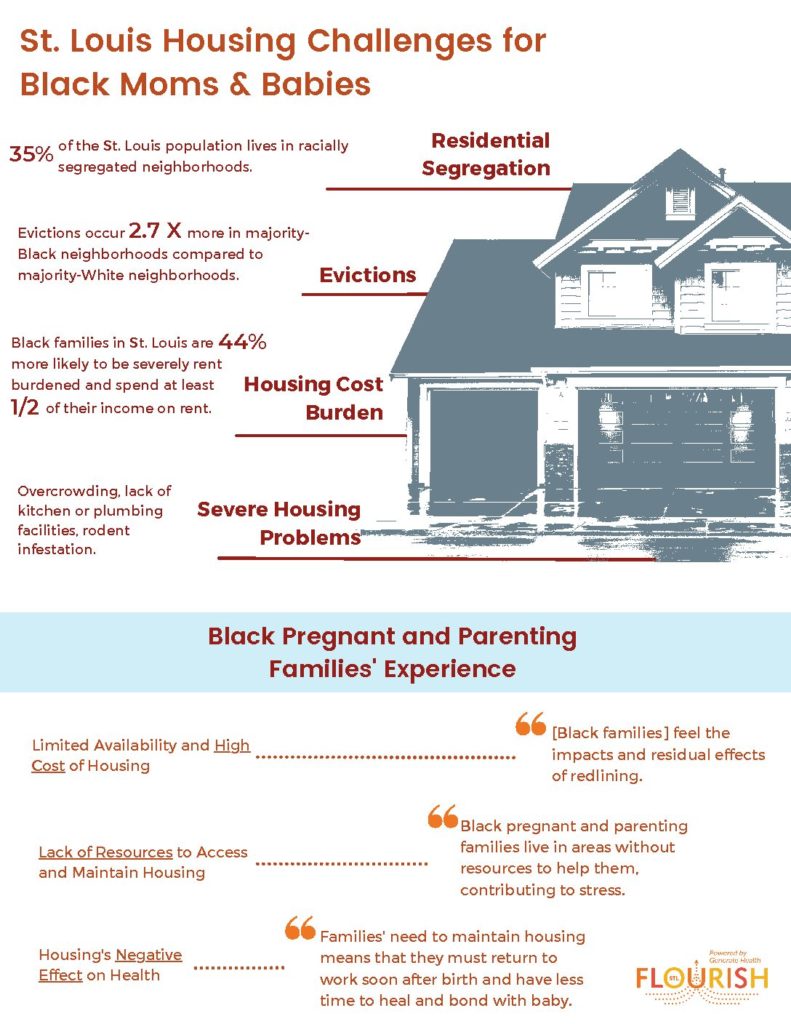
Black pregnant and parenting families in St. Louis experience stress due to housing costs, housing availability, and lack of resources in neighborhoods. Stressors such as high rent costs, evictions, over-crowding, and lack of kitchen or plumbing facilities can cause health problems. Pregnant people and their families need quality, affordable housing and landlords that will accommodate their needs so they can spend time caring for their baby.
Additional Resources
Click Red Button to View Infographic
Double-Click Red Button to Download Infographic
Home Ownership
Home ownership is defined as the percentage of occupied housing units that are owned.(Source: Census)
62.5
67.0
66.8
Severe Housing Costs Burden
Severe housing cost burden is defined as the percentage of households that spend 50% or more of their household income on housing. (Source: County Health Rankings)
13.8
11.0
10.7
Severe Housing Problems
Severe housing problems is defined as the percentage of households with at least 1 of 4 housing problems: overcrowding, high housing costs, lack of kitchen facilities, or lack of plumbing facilities. (Source: HUD Office of Policy Development and Research)
15.0
13.1
17.3
Evictions
Evictions are defined as the percentage of evictions per 100 renter homes in an area. (Source: Eviction Lab)
3.99
2.85
2.34
Social Determinants of Health
Community Conditions
Feeling a lack of community support or trust and safety in a community negatively affects the health of Black pregnant and parenting families. In St. Louis city alone, there are over 24,000 vacant properties, including buildings and lots. Community conditions that affect the overall vibe of a neighborhood include: overgrown lots, crumbling buildings, decreased property values and disparate amenities. These conditions pose a serious public health and safety risks for St. Louis residents. While St. Louis’ median home value surpasses Missouri and the United States, historic practices of redlining in St. Louis have resulted in lower property values in predominately Black neighborhoods. Delmar Boulevard, known as the dividing line in St. Louis, lays bare the stark disparities. Median home values south of Delmar –in predominantly white neighborhoods — being four times greater than those north of Delmar, predominately Black neighborhoods. To thrive, families need more access to green spaces, healthy food options, community activities, and community centers. Investing in community resources will strengthen the support network for pregnant and parenting families.
Additional Resources
Click Red Button to View Infographic
Double-Click Red Button to Download Infographic
Residential Segregation
Residential segregation is defined as the percentage of residents that live in racially segregated census tracts in the St. Louis region. Racially segregated census tracts are census tracts in which the population is either more than 90% black or more than 90% white. (Source: STL Equity Indicators; Census)
32.5
X.X
X.X
Vacant Lots
Vacant lots are defined as the percentage of land parcels without an owner or renter living on the property. (Source: Census, St. Louis Vacancy Collaborative)
6.4
9.90
10.6
Median Home Values
Median home value is defined as the average value of a home owned by an individual. (Source: AHRQ Social Determinants of Health Database)
$161,000
$116,000
$146,000
Social Determinants of Health
Transportation
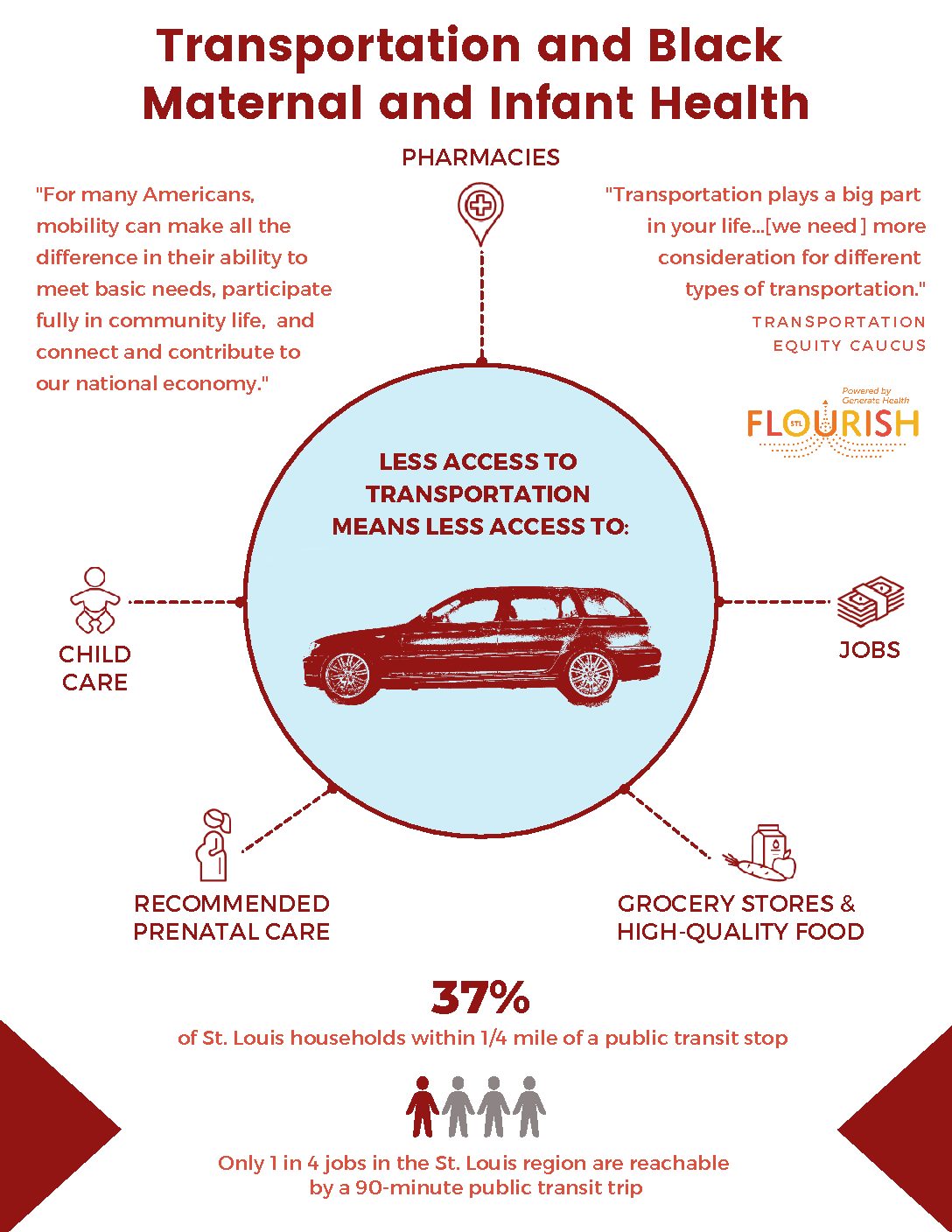
Unreliable transportation can negatively affect the health of Black women and birthing people by causing them to arrive late to medical appointments or miss them all together. This can affect doctor-patient relationships and the quality of care that pregnant and parenting families receive. Despite our public transit infrastructure, St. Louis residents still struggle to access reliable transportation, requesting nearly 40% of the transportation assistance calls across the state. Since 80% of all public transit users in St. Louis are Black, Black St. Louisans face this burden disproportionately. Black pregnant and parenting families need reliable transportation designed with their logistical and financial needs in mind.
Click Red Button to View Infographic
Double-Click Red Button to Download Infographic
Transportation Assistance Requests
Transportation assistance requests is defined as the number of resource referral calls requesting transportation services in 2021. (Source: 2-1-1 Counts MO)
2,401
6,561
XX
Housing Units with No Motor Vehicles
Housing units with no motor vehicles is defined as the percentage of housing units without a motor vehicle (source: Environmental Public Health Tracking Network)
13.5
6.18
6.35
Transportation to Work
Transportation to work is defined as the percentage of workers over 16 years of age that use public transportation (Source: National Environmental Public Health Tracking Network)
5.9
0.41
0.92
Commute Time
Commute time is defined as the average number of minutes for one way commute time for workers 16 years of age and older for all travel modes. (Source: National Environmental Public Health Tracking Network)
24
23.62
23.29
Social Determinants of Health
Food Access
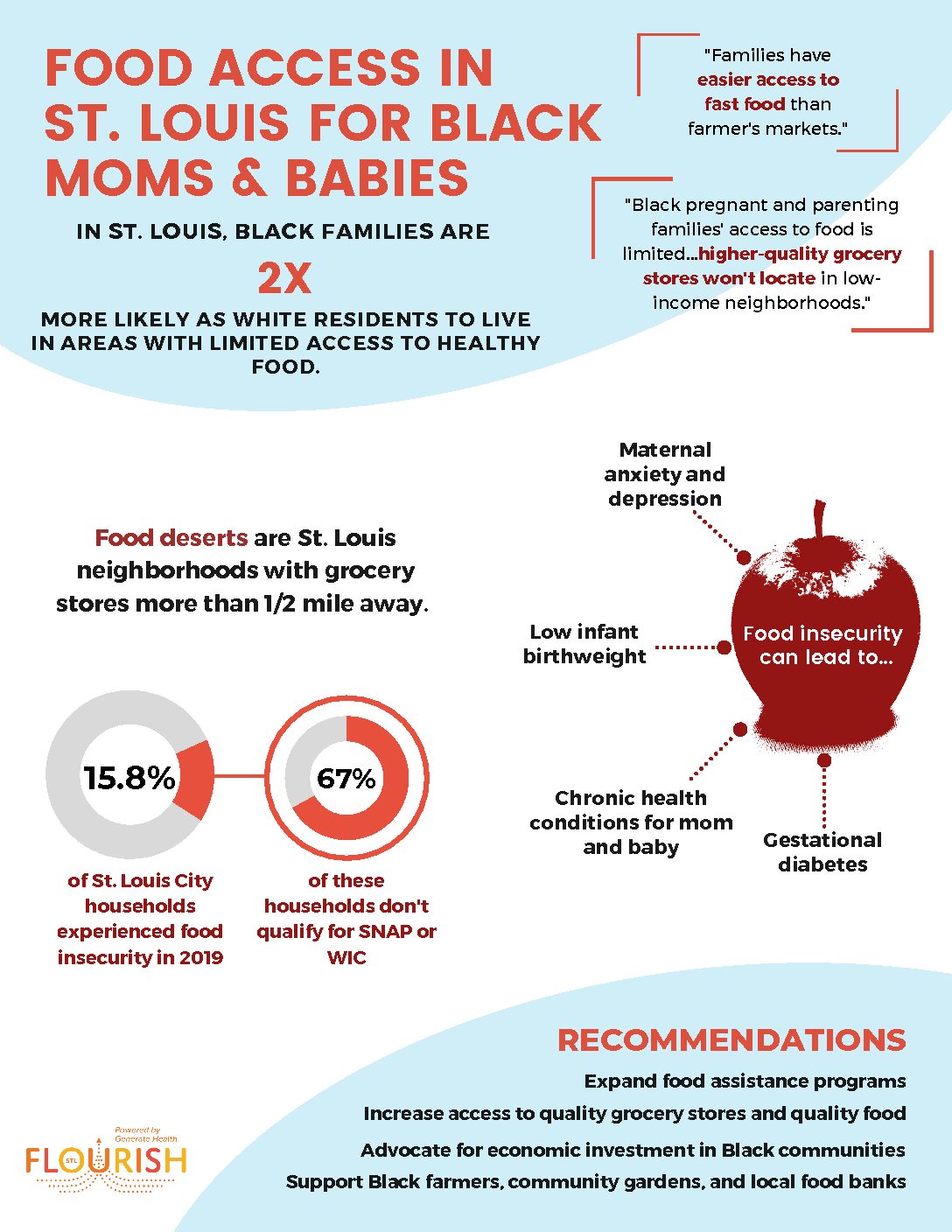
Inadequate access to healthy foods affects Black pregnant and parenting families’ health. Access to grocery stores increases access to fresh, healthy foods which can prevent or reduce the burden of food-related illnesses. Without proper nutrition, moms and babies are at a higher risk for poor health outcomes. Communities’ access to food is interconnected to its access to other social determinants of health such as transportation and housing. Providing increased access to quality grocery stores and fresh foods will improve the health of pregnant and parenting families.
Additional Resources
Click Red Button to View Infographic
Double-Click Red Button to Download Infographic
Low Income & Low Access to Food
Low income & low access to food is defined as the percentage of census tracts with low-income residents who have low access to healthy food. Low access to healthy food is defined as residents who live 1/2 mile or further from a supermarket, supercenter, or large grocery store. (Source: USDA Economic Research Atlas)
36.9
32.6
27.9
Access to Grocery Store
Access to grocery store is defined as the percentage of households with low access to grocery stores. (Source: USDA Economic Research Atlas)
16.4
20.6
23.1
Food Insecurity
Food insecurity is defined by the United States Department of Agriculture as a lack of consistent access to enough food to sustain an active, healthy life for all of a household’s members, and limited or uncertain availability of nutritionally adequate foods as a result of economic and social conditions. (Source: Feeding America)
11.5
13.2
10.9